BehaviorScan is an advanced automated rodent monitoring system designed to facilitate behavioral research in mice and rats. With its high-resolution tracking capabilities and real-time data acquisition, BehaviorScan offers a comprehensive solution for monitoring various behavioral parameters. Its user-friendly interface and customizable testing protocols make it an essential tool for researchers seeking accurate and efficient behavioral analysis.
ConductScience offers the BehaviorScan: Automated Rodent Monitoring System.
10% off with your subscription Membership
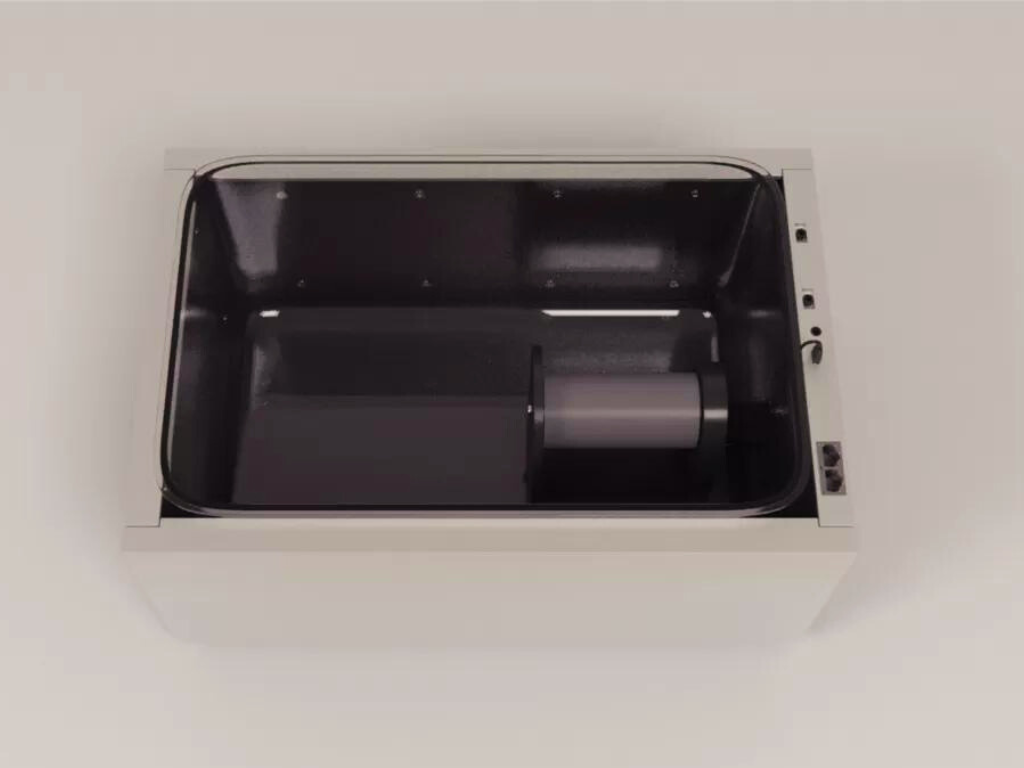


The BehaviorScan Automated Rodent Monitoring System is a state-of-the-art research tool designed by ConductScience. This innovative system is specifically designed to enhance behavioral research in rodents. By providing high-resolution tracking and real-time data acquisition, BehaviorScan enables researchers to gain valuable insights into rodent behavior.
BehaviorScan offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies system setup, operation, and data analysis. Researchers can easily customize testing protocols according to their specific experimental requirements, ensuring accurate and targeted data collection.
The system excels in multi-parameter monitoring, capturing a wide range of behavioral parameters simultaneously. It allows researchers to track and analyze parameters such as locomotion, exploratory behavior, social interactions, anxiety-related behaviors, and more. By automating the monitoring process, BehaviorScan eliminates the need for manual observation, saving time and reducing potential observer bias.
BehaviorScan seamlessly integrates with other research tools and software, facilitating comprehensive data analysis. It offers connectivity options such as USB, Ethernet, etc., enabling easy data transfer and compatibility with commonly used software and analysis platforms.
Behavioral research plays a crucial role in understanding various aspects of rodent behavior, ranging from exploratory patterns to social interactions and cognitive abilities. Conducting comprehensive behavioral analysis requires accurate and efficient monitoring systems that capture the complexity of rodent behavior. BehaviorScan: Automated Rodent Monitoring System is designed to meet these research demands by offering advanced tracking capabilities, real-time data acquisition, and user-friendly features.
BehaviorScan is widely used in research fields such as neuroscience, psychology, pharmacology, and behavioral genetics. It is utilized in studies investigating various aspects of rodent behavior, including but not limited to:
The BehaviorScan system includes the following components:
BehaviorScan enables a wide range of behavioral tests, including:
BehaviorScan offers researchers a comprehensive solution for automated rodent behavioral monitoring. Its high-resolution tracking capabilities and real-time data acquisition provide valuable insights into rodent behavior. By automating the monitoring process, BehaviorScan enhances research efficiency and minimizes observer bias.
To use BehaviorScan, follow these general steps:
BehaviorScan: Automated Rodent Monitoring System by ConductScience is a sophisticated research tool designed to enhance behavioral analysis in mice and rats. With its high-resolution tracking capabilities, real-time data acquisition, and user-friendly features, BehaviorScan offers researchers a comprehensive solution for automated rodent behavioral monitoring. Its customizable testing protocols, multi-parameter monitoring, and data integration capabilities make it an essential tool for various fields of research.
The BehaviorScan Automated Rodent Monitoring System provides researchers with a powerful and efficient tool for studying rodent behavior. By automating the monitoring process and offering high-resolution tracking and real-time data acquisition, BehaviorScan enhances research efficiency and accuracy. With its user-friendly interface, customizable testing protocols, and compatibility with other research tools, BehaviorScan proves to be an indispensable asset for researchers in neuroscience, psychology, pharmacology, and behavioral genetics.
| Species | Mouse, Rat |
|---|---|
| Brand | Afasci |
You must be logged in to post a review.
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.