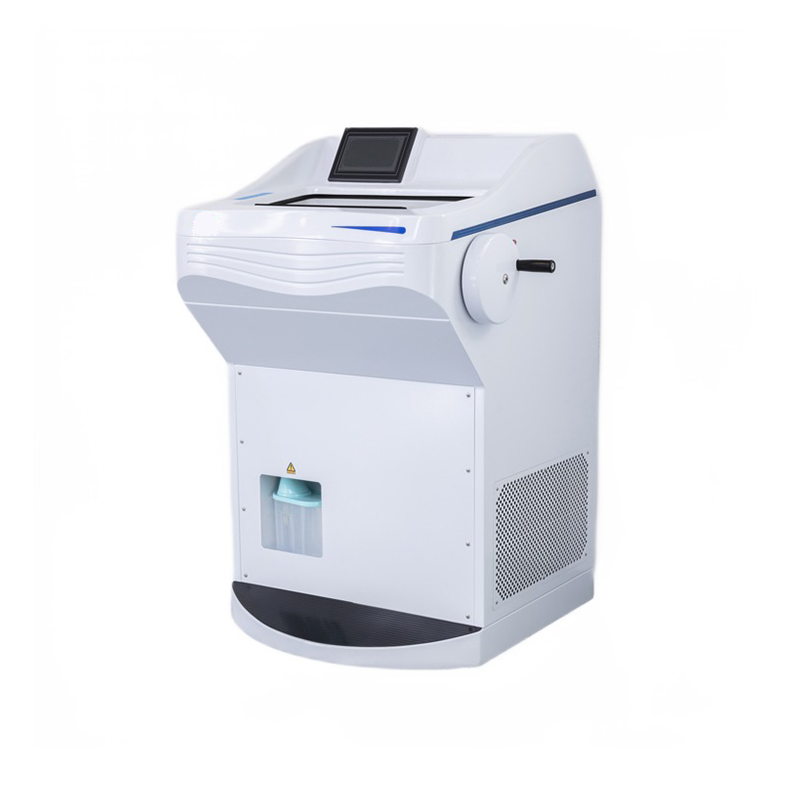
A cryostat microtome is a precision instrument designed for the sectioning of frozen biological specimens in laboratory settings. It combines freezing technology with a microtome, allowing users to obtain thin slices of tissues for various applications in research, pathology, and diagnostics.
The Cryostat Microtome excels in preserving the structural integrity of delicate samples by maintaining low temperatures during the sectioning process. It is commonly utilized in histology and pathology laboratories for preparing tissue specimens for microscopic analysis. This specialized equipment is crucial for achieving high-quality, thin sections suitable for detailed examination under a microscope. Upgrade your laboratory capabilities with our advanced Cryostat Microtome, designed for efficient and precise frozen sectioning.
$0.00
10% off with your subscription Membership


Specimen retraction function: prevents specimens from accidental blade damage. This function can be turned off.
The unit can be defrosted manually or by a controlled time setting.

A cryostat microtome is a specialized instrument used for cutting thin sections of frozen specimens, typically for histology and pathology research. The main parts of a cryostat microtome include:
Freezing Chamber:
Microtome Sectioning Mechanism:
Specimen Holder:
Temperature Control System:
Knife Holder and Blade:
Defrosting Mechanism:
Display and Controls:
Illumination System:
Waste Collection System:
Vacuum System:
Storage Compartments:
Manual Cryostat Microtome:
Semi-Automatic Cryostat Microtome:
Fully Automatic Cryostat Microtome:
Freezing Microtome:
Infrared Cryostat Microtome:
Digital Cryostat Microtome:
Cryostat Microtome with UV Disinfection:
Clinical Cryostat Microtome:
Research Cryostat Microtome:
Strengths:
Precision Sectioning: One of the key strengths is its ability to provide high-precision sectioning of frozen tissue samples. This is crucial in histology and pathology applications where thin and accurate sections are required for analysis.
Cryogenic Cooling: The incorporation of cryogenic cooling ensures that the samples remain frozen during the sectioning process. This is particularly advantageous for preserving the integrity of delicate structures within the tissue.
Versatility: Cryostat Rotary Freezing Microtomes are versatile instruments that can handle a variety of sample types, including soft and hard tissues. This makes them suitable for a wide range of research and diagnostic applications.
Speed: Compared to traditional microtomes, cryostat rotary microtomes can provide quicker results due to the rapid freezing and sectioning process.
Reduced Artifacts: The frozen sectioning process helps reduce artifacts that may be introduced by other methods, allowing for more accurate analysis of tissue structures.
Limitations:
Cost: Cryostat Rotary Freezing Microtomes can be relatively expensive to purchase and maintain, making them less accessible for some research labs or smaller institutions with budget constraints.
Complex Operation: Operating a cryostat microtome may require specialized training due to its complex design and the need to manage cryogenic temperatures. This can limit its use to trained personnel.
Sample Size Restrictions: The size of the samples that can be accommodated may be limited by the dimensions of the cryostat chamber. Larger specimens may need to be processed differently.
Maintenance Requirements: Cryostat microtomes require regular maintenance, including defrosting and cleaning, to ensure optimal performance. Failure to maintain the instrument properly can lead to issues with sectioning quality.
| Brand | Roundfin |
|---|---|
| Net weight | 150 kg |
| Size | 800*700*1190 mm |
| Gross weight | 175 kg |
| Packing size | 860*920*1480 mm |
| Voltage and frequency | AC220V±10%,50Hz(Standard) |
| Power | 500W |
| Noise | 50Db(A) |
| Refrigerany | R404A |
| Type for blade holder | Yes |
| Waste Cleaner | Yes |
| Handwheel lock | 16 positions locked |
| Certification | CE |
| Other remarks | OEM/custom-made accepted |
You must be logged in to post a review.
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.